X C V I I
defexpoindia
Sep 13, 2025 · 5 min read
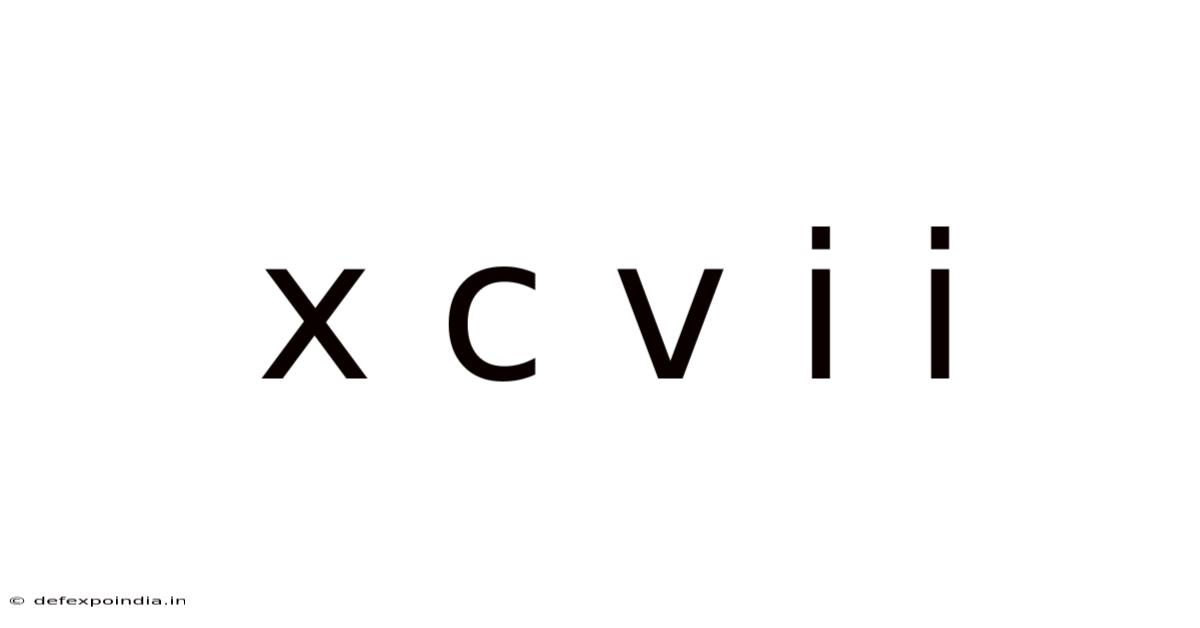
Table of Contents
Unraveling the Mystery: A Deep Dive into XCVII
The Roman numeral XCVII often sparks curiosity, especially for those unfamiliar with the ancient Roman system of numerical notation. This article will delve into the meaning and composition of XCVII, explaining its structure, exploring its historical context, and providing a comprehensive understanding for both beginners and those seeking a deeper appreciation of Roman numerals. We'll cover everything from the basic building blocks to advanced applications, making sure to leave no stone unturned in our exploration of this fascinating numerical representation.
Understanding Roman Numerals: A Foundation
Before we dissect XCVII, let's establish a firm understanding of the Roman numeral system. This system, used extensively in ancient Rome and still found in various applications today (like clock faces, chapter numbering in books, and copyright dates), relies on seven key symbols:
- I: Represents 1
- V: Represents 5
- X: Represents 10
- L: Represents 50
- C: Represents 100
- D: Represents 500
- M: Represents 1000
The beauty of the Roman system lies in its additive and subtractive principles. Numbers are formed by combining these symbols. When a smaller symbol precedes a larger one, it's subtracted (e.g., IV = 4, because I (1) is subtracted from V (5)). When a smaller symbol follows a larger one, it's added (e.g., VI = 6, because I (1) is added to V (5)).
Deconstructing XCVII: A Step-by-Step Approach
Now, let's break down XCVII step-by-step:
-
XC: This combination represents 90. The X (10) preceding the C (100) indicates subtraction, resulting in 100 - 10 = 90.
-
V: This symbol simply represents 5.
-
II: This represents 2 (I + I = 2).
Therefore, XCVII is the Roman numeral representation of 97 (90 + 5 + 2 = 97).
Historical Context and Applications of Roman Numerals
The Roman numeral system wasn't just a mathematical tool; it was deeply ingrained in Roman culture and society. Inscriptions on buildings, monuments, and even everyday objects frequently utilized Roman numerals. Their widespread use extended beyond simple counting; they were integral to recording dates, marking milestones, and even expressing quantities in various contexts. While the system eventually gave way to the more efficient Hindu-Arabic system we use today, Roman numerals remain a testament to the ingenuity and lasting impact of Roman civilization. Their continued presence in modern applications, though limited, highlights their enduring legacy.
Advanced Concepts in Roman Numerals: Beyond the Basics
While the basic principles are relatively straightforward, the Roman numeral system does possess some intricacies:
-
Repeated Symbols: The same symbol can be repeated up to three times consecutively. For example, III represents 3, and XXX represents 30. However, you wouldn't write IIII for 4; instead, you'd use IV.
-
Subtractive Notation: The subtractive principle, as seen in IV (4), IX (9), XL (40), XC (90), CD (400), and CM (900), is crucial for efficient representation and avoids overly long sequences of symbols.
-
No Zero: The Roman system lacked a symbol for zero. This absence significantly impacted the complexity of certain mathematical operations, particularly those involving place value.
-
Large Numbers: Representing extremely large numbers required lengthy strings of symbols, making calculations cumbersome. This limitation further contributed to the eventual adoption of the Hindu-Arabic system.
Comparing Roman Numerals with the Hindu-Arabic System
The Hindu-Arabic numeral system, the system we use daily, offers significant advantages over the Roman system:
-
Place Value: The Hindu-Arabic system utilizes a place value system, where the position of a digit determines its value. This allows for the concise representation and manipulation of even extremely large numbers. Roman numerals lack this crucial element.
-
Zero: The inclusion of zero as a placeholder symbol revolutionized mathematics, enabling more efficient calculations and the development of more advanced mathematical concepts.
-
Ease of Calculation: Performing arithmetic operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication, division) is significantly easier with the Hindu-Arabic system compared to the Roman system.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about XCVII and Roman Numerals
Q: Are there any variations in Roman numeral notation?
A: While the standard rules are consistent, minor variations existed throughout history and across different regions. Some inscriptions might use unconventional subtractive forms or employ less common symbols.
Q: Why did Roman numerals eventually fall out of favor?
A: The Hindu-Arabic system's inherent efficiency in representing and manipulating numbers, especially larger ones, made it far superior for practical applications, leading to its widespread adoption.
Q: Can I use XCVII in a formal context today?
A: While perfectly valid, its use in modern formal contexts might be limited to specific situations like chapter numbering, copyright dates, or where a classical aesthetic is desired. Using the Arabic numeral 97 is generally preferred for clarity and ease of understanding in most contemporary applications.
Q: How can I convert Roman numerals to Arabic numerals?
A: Understanding the basic symbols and the additive/subtractive principles is key. Break down the Roman numeral into its constituent parts, applying the rules as explained earlier, and sum the values to arrive at the equivalent Arabic numeral.
Q: Are there any resources available to further improve my understanding of Roman numerals?
A: Various online resources, educational websites, and textbooks offer detailed explanations and exercises to strengthen your knowledge and skills in working with Roman numerals.
Conclusion: The Enduring Appeal of XCVII and Roman Numerals
XCVII, representing 97 in Roman numerals, serves as a microcosm of a rich and complex system. Its decomposition reveals the elegance and inherent logic of Roman numerical notation. Though surpassed by the more efficient Hindu-Arabic system in widespread use, Roman numerals continue to hold a special place in history and culture, reminding us of the ingenuity of past civilizations and offering a unique window into their mathematical understanding. Their continued appearance in modern life, even in a limited capacity, speaks to their enduring appeal and historical significance. Understanding XCVII and the Roman numeral system as a whole provides not only a valuable historical perspective but also enhances mathematical appreciation and cultivates a deeper understanding of numerical representation across different systems.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about X C V I I . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.