What Is Xxii In Numbers
defexpoindia
Sep 22, 2025 · 6 min read
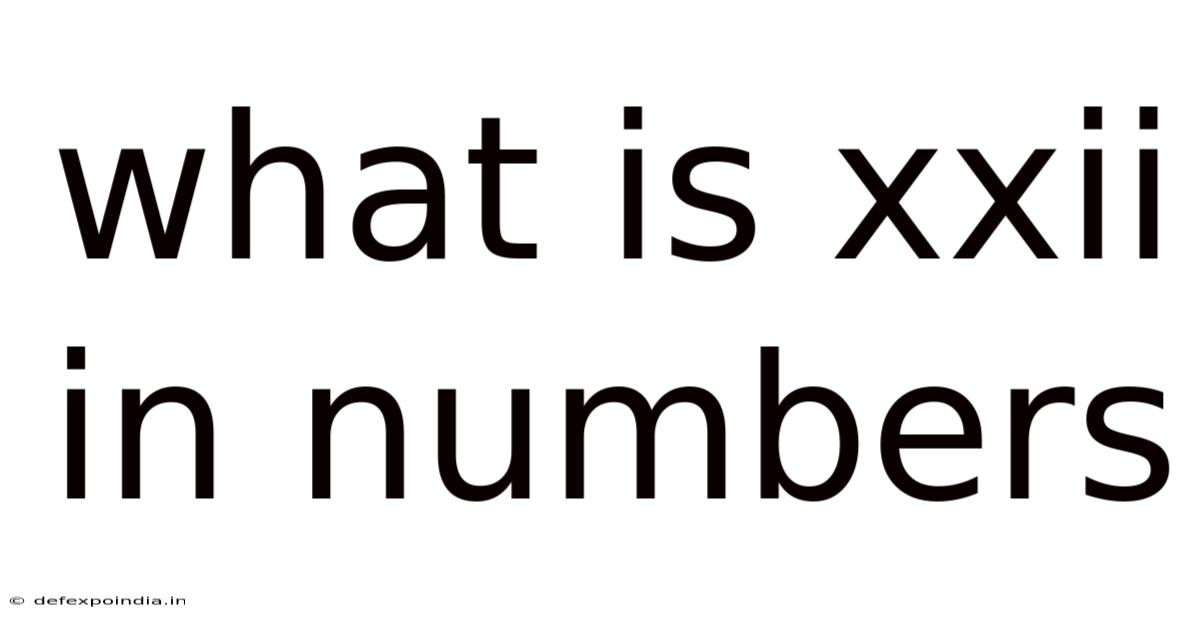
Table of Contents
What is XXII in Numbers? Understanding Roman Numerals and Their Applications
Are you curious about the meaning of XXII? This seemingly simple question opens the door to a fascinating world of ancient number systems and their continued relevance in modern society. This comprehensive guide will explore what XXII represents in modern numerical notation, delve into the history and structure of Roman numerals, and demonstrate their practical applications today. We'll also tackle some common questions and misconceptions surrounding this ancient system of counting.
Understanding Roman Numerals: A Historical Overview
Roman numerals are a system of numerical notation originating in ancient Rome. Unlike the decimal system (base-10) we use today, Roman numerals utilize a combination of letters to represent numerical values. This system, while seemingly complex at first, relies on a straightforward set of rules and principles. The system's longevity is a testament to its effectiveness, even though it's largely been replaced by the more efficient decimal system.
The core of the Roman numeral system lies in seven basic symbols:
- I: 1
- V: 5
- X: 10
- L: 50
- C: 100
- D: 500
- M: 1000
These symbols are combined and manipulated to represent numbers larger than 1000. This process isn't as arbitrary as it might first appear, with roots in ancient Roman practices and conventions. There are theories connecting the shapes of the letters to the quantities they represent, possibly linked to counting methods involving fingers and hands. For example, 'V' could visually represent the spread of a hand, mirroring the quantity of five.
Deciphering XXII: The Step-by-Step Breakdown
Now, let's focus on the specific question: What is XXII in numbers?
XXII is composed of three distinct Roman numeral symbols:
- X: Represents 10
- X: Represents 10
- II: Represents 2 (I + I)
Therefore, XXII is simply 10 + 10 + 2 = 22. The answer is straightforward once you understand the fundamental building blocks of the Roman numeral system.
The Rules of Roman Numeral Construction
To fully grasp the meaning of XXII and other Roman numerals, let’s examine the rules governing their construction:
- Additive Principle: When a smaller numeral is placed before a larger numeral, it is subtracted from the larger numeral. For example, IV (4) is 5 - 1, and IX (9) is 10 - 1.
- Subtractive Principle: When a smaller numeral is placed after a larger numeral, it is added to the larger numeral. For example, VI (6) is 5 + 1, and XI (11) is 10 + 1.
- Repetitions: Symbols can be repeated up to three times consecutively to express multiples. For instance, III represents 3, XX represents 20, and CCC represents 300. However, you cannot repeat a numeral four times. Instead, subtractive notation is used (e.g., IV instead of IIII).
- Specific Combinations: Certain specific combinations are used, for example, IV (4), IX (9), XL (40), XC (90), CD (400), and CM (900). These are essentially shortcuts to avoid lengthy repetitions.
Understanding these rules is crucial for accurately interpreting and constructing Roman numerals. They are not arbitrary but follow a logical structure that, once mastered, makes working with Roman numerals surprisingly intuitive.
Beyond XXII: Exploring Larger Roman Numerals
While XXII is a relatively small number, the Roman numeral system can be extended to represent significantly larger quantities. Numbers beyond 1000 are represented using the following extensions:
- M: 1000
- V̅: 5000 (V with a bar over it)
- X̅: 10,000 (X with a bar over it)
- L̅: 50,000 (L with a bar over it)
- C̅: 100,000 (C with a bar over it)
- D̅: 500,000 (D with a bar over it)
- M̅: 1,000,000 (M with a bar over it)
These barred numerals allow the representation of considerably larger numbers. Even larger numbers can be represented using additional bars or other notations depending on the context and convention. The system, while not as concise as the decimal system, possesses a certain elegance and historical significance.
Applications of Roman Numerals in the Modern World
Despite the widespread adoption of the decimal system, Roman numerals continue to find practical applications in various contexts:
- Clock Faces: Many analog clocks use Roman numerals for the hours, lending a classic and elegant aesthetic.
- Outlines and Lists: Roman numerals are occasionally used to organize outlines, chapters, or lists, particularly in formal documents.
- Copyright Dates: Roman numerals are sometimes seen in copyright notices, providing a more formal and stylistic touch.
- Monarch Names: Kings and queens are often designated with Roman numerals (e.g., Louis XIV).
- Super Bowl Numbers: The Super Bowl games are numbered using Roman numerals.
- Building Designations: Roman numerals can be used in building numbers and architectural details.
- Movie Credits: In older movies, credits sometimes use Roman numerals to denote years.
These examples demonstrate that Roman numerals, while not the primary number system for everyday calculations, maintain a niche presence and a particular aesthetic appeal.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Why are Roman numerals still used today?
A: Roman numerals persist primarily for their historical significance and aesthetic value. Their use in specific contexts, like clock faces or copyright notices, enhances formality and a classic look. While they are not efficient for complex calculations, they maintain a symbolic and stylistic role.
Q: Are there any limitations to the Roman numeral system?
A: Yes. The Roman numeral system lacks a true zero, making certain mathematical operations more challenging. It's also less efficient than the decimal system for large numbers and complex calculations. The lack of a placeholder for zero significantly impacts its ability to represent numbers concisely.
Q: Can Roman numerals represent fractions or decimal numbers?
A: Traditionally, the Roman numeral system doesn't have a built-in mechanism for representing fractions or decimals. While some historical adaptations existed, they were not standard and lacked widespread usage. The system is primarily designed for representing whole numbers.
Q: What is the largest number that can be represented using standard Roman numerals?
A: Technically, there is no theoretical upper limit. You could create extremely large numbers using a combination of the basic symbols and the barred notation for higher multiples of 1000. However, practically, the system becomes cumbersome and unwieldy for extremely large numbers.
Conclusion: The Enduring Legacy of Roman Numerals
XXII, representing the number 22, provides a gateway to understanding the intriguing system of Roman numerals. While largely replaced by the decimal system for everyday use, Roman numerals maintain a significant presence due to their historical importance and enduring aesthetic appeal. Their continued use in various contexts showcases the enduring legacy of this ancient numbering system, reminding us of the rich history embedded in seemingly simple symbols. From clock faces to formal documents, the Roman numeral system continues to contribute a unique charm and a touch of classical elegance to the modern world. Understanding its structure and applications allows for a deeper appreciation of its historical significance and continued relevance.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is Xxii In Numbers . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.