What Is 20 In Decimal
defexpoindia
Sep 13, 2025 · 6 min read
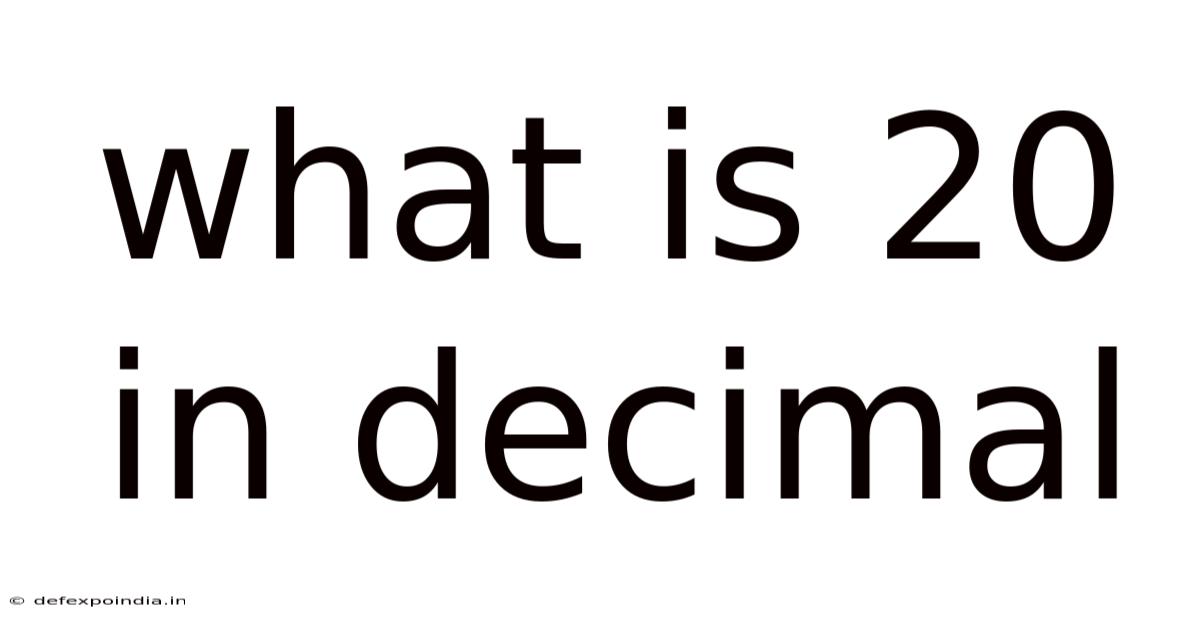
Table of Contents
What is 20 in Decimal? A Deep Dive into Number Systems
The question, "What is 20 in decimal?" might seem trivial at first glance. The answer, of course, is 20. However, this seemingly simple question opens a door to a fascinating exploration of number systems, their foundations, and how we represent quantities. This article will delve into the concept of decimal numbers, exploring its history, its underlying principles, and comparing it to other number systems to fully illuminate the significance of the number 20 within the decimal framework.
Understanding the Decimal System (Base-10)
The decimal system, also known as the base-10 system, is the most commonly used number system globally. Its foundation lies in the use of ten digits: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9. The power of the decimal system stems from its positional notation, meaning the value of a digit depends on its position within the number. Each position represents a power of 10.
Let's break down the number 20 to illustrate this:
- 20 can be written as (2 x 10¹) + (0 x 10⁰).
Here:
- 10¹ represents the tens place (10 to the power of 1, which is 10).
- 10⁰ represents the ones place (10 to the power of 0, which is 1).
Therefore, the digit '2' in the tens place signifies two tens (2 x 10 = 20), and the digit '0' in the ones place signifies zero ones (0 x 1 = 0). Adding these together gives us 20. This positional system allows us to represent arbitrarily large numbers using a limited set of digits.
The History of the Decimal System
The widespread adoption of the decimal system is largely attributed to the fact that humans have ten fingers. This natural counting mechanism likely influenced the development of base-10 counting in many ancient civilizations. While other bases were used (and still are), the decimal system eventually gained prominence due to its relative simplicity and efficiency. Ancient civilizations like the Egyptians, Babylonians, and Indians all used variations of decimal systems, gradually refining the notation and algorithms for arithmetic operations. The modern decimal system, with its place value notation, solidified over many centuries, thanks to contributions from numerous mathematicians and cultures.
Comparing Decimal to Other Number Systems
To appreciate the uniqueness of the decimal system and the meaning of 20 within it, let's compare it to other number systems:
-
Binary (Base-2): The binary system uses only two digits: 0 and 1. This system is fundamental to computer science and digital electronics. The number 20 in decimal is equivalent to 10100 in binary. This represents (1 x 2⁴) + (0 x 2³) + (1 x 2²) + (0 x 2¹) + (0 x 2⁰) = 16 + 4 = 20.
-
Octal (Base-8): The octal system utilizes eight digits: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7. It's sometimes used in computing as a more human-readable alternative to binary. 20 in decimal is 24 in octal (2 x 8¹ + 4 x 8⁰ = 16 + 4 = 20).
-
Hexadecimal (Base-16): Hexadecimal uses sixteen digits: 0-9 and A-F (where A represents 10, B represents 11, and so on). It's commonly used in computer programming and color codes. 20 in decimal is 14 in hexadecimal (1 x 16¹ + 4 x 16⁰ = 16 + 4 = 20).
The Significance of Positional Notation
The core strength of the decimal system, and indeed any positional number system, lies in its ability to represent numbers concisely and efficiently using a limited number of symbols. Without positional notation, representing large numbers would require an exponentially larger number of unique symbols. The concept of place value, where the position of a digit determines its contribution to the overall value, allows for scalability and streamlined arithmetic operations. This system facilitates addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division with relative ease, forming the foundation of mathematical computation as we know it.
Beyond the Basics: Decimal Fractions and Scientific Notation
The decimal system extends beyond whole numbers to include decimal fractions. These fractions are represented using a decimal point to separate the whole number part from the fractional part. For example, 20.5 represents twenty and a half. Each position to the right of the decimal point represents a negative power of 10. 20.5 can be expressed as (2 x 10¹) + (0 x 10⁰) + (5 x 10⁻¹).
For extremely large or small numbers, scientific notation offers a compact representation. This notation expresses a number as a product of a number between 1 and 10 and a power of 10. For instance, 20,000 can be written as 2 x 10⁴, and 0.0002 can be written as 2 x 10⁻⁴. This simplifies calculations and improves readability for numbers spanning many orders of magnitude.
Mathematical Operations with Decimal Numbers
The decimal system seamlessly integrates with standard mathematical operations. The algorithms for addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division are based on the principles of place value and the properties of the base-10 system. These algorithms are taught in elementary schools and form the bedrock of more advanced mathematical concepts. The ease with which these operations can be performed is a significant advantage of the decimal system.
Decimal Numbers in Everyday Life
Decimal numbers are ubiquitous in our daily lives. From money (dollars and cents), to measurements (meters, centimeters, kilograms), to time (hours, minutes, seconds), the decimal system is deeply ingrained in our societal systems. Its pervasiveness highlights its practicality and efficiency in representing and manipulating quantitative information. Understanding the decimal system is crucial for navigating the numerical aspects of daily life.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: Why is the decimal system so prevalent? A: The decimal system's widespread use is largely attributed to the fact that humans have ten fingers, making it a natural counting system. Its relative simplicity and efficiency in representing and manipulating numbers have further solidified its dominance.
-
Q: Are there any disadvantages to the decimal system? A: While the decimal system is highly effective, it's not ideal for all applications. In computer science, the binary system is fundamental due to the inherent on/off nature of electronic circuits. Other bases can offer advantages in specific contexts.
-
Q: How do I convert numbers from other bases to decimal? A: To convert a number from another base to decimal, you multiply each digit by the corresponding power of the base and sum the results. For example, to convert the binary number 1011 to decimal: (1 x 2³) + (0 x 2²) + (1 x 2¹) + (1 x 2⁰) = 8 + 0 + 2 + 1 = 11.
-
Q: What is the significance of zero in the decimal system? A: Zero plays a critical role in the decimal system as a placeholder. It signifies the absence of a quantity in a particular position, allowing us to distinguish between numbers like 20 and 2. Without zero, positional notation wouldn't function effectively.
Conclusion
The answer to "What is 20 in decimal?" is, simply, 20. However, understanding this seemingly straightforward answer requires a deeper exploration of the decimal system itself. This article has highlighted the historical context, fundamental principles, and practical applications of this ubiquitous number system. By comparing it to other number systems and examining its underlying structure, we can truly appreciate the power and significance of the decimal system in shaping our mathematical understanding and daily lives. The seemingly simple number 20, therefore, serves as a gateway to a vast and fascinating world of numerical representation and computation. From its origins in the natural world to its role in complex scientific calculations, the decimal system remains a cornerstone of our modern world.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is 20 In Decimal . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.