8 3/8 As A Decimal
defexpoindia
Sep 14, 2025 · 5 min read
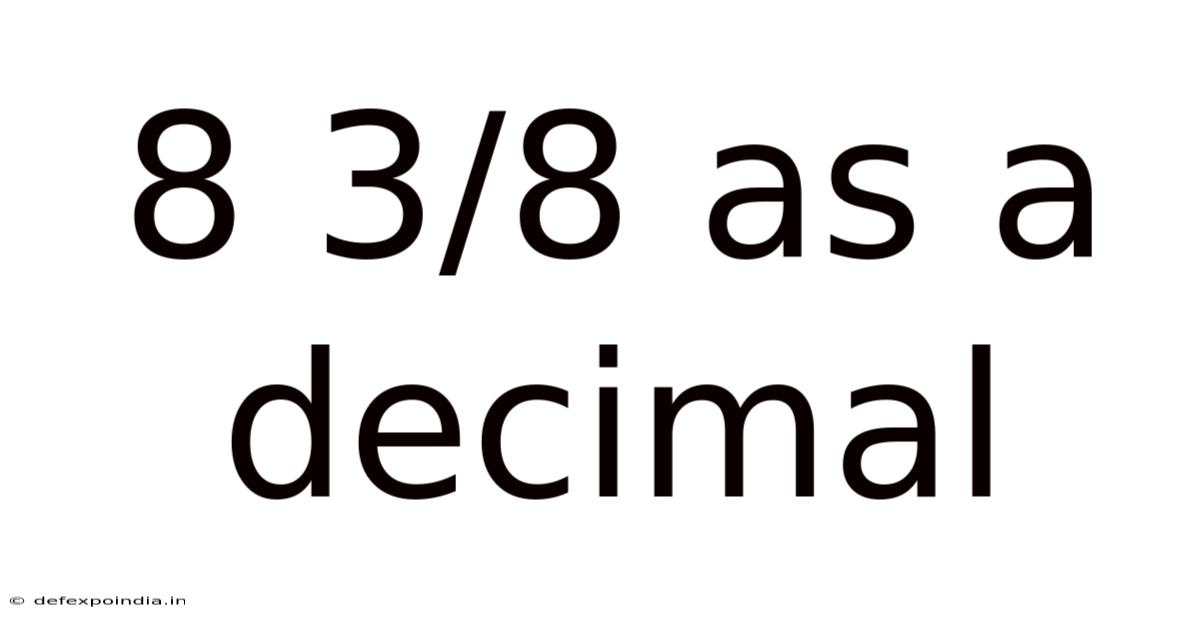
Table of Contents
8 3/8 as a Decimal: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding how to convert fractions to decimals is a fundamental skill in mathematics, crucial for various applications from everyday calculations to advanced scientific computations. This article provides a detailed explanation of how to convert the mixed number 8 3/8 into its decimal equivalent, exploring different methods and delving into the underlying mathematical principles. We'll also address common questions and misconceptions surrounding decimal conversions.
Introduction: Understanding Mixed Numbers and Decimals
Before diving into the conversion process, let's briefly review the concepts of mixed numbers and decimals. A mixed number combines a whole number and a fraction, such as 8 3/8. This represents 8 whole units plus an additional 3/8 of a unit. A decimal, on the other hand, expresses a number using a base-ten system, with digits placed to the right of the decimal point representing fractions of powers of ten (tenths, hundredths, thousandths, and so on). Converting a mixed number to a decimal involves expressing the fractional part as a decimal and then adding it to the whole number.
Method 1: Converting the Fraction to a Decimal Directly
The most straightforward approach to converting 8 3/8 to a decimal involves focusing on the fractional part, 3/8. To convert a fraction to a decimal, we simply divide the numerator (the top number) by the denominator (the bottom number).
-
Divide the numerator by the denominator: 3 ÷ 8 = 0.375
-
Add the whole number: 8 + 0.375 = 8.375
Therefore, 8 3/8 expressed as a decimal is 8.375.
Method 2: Converting the Fraction using Equivalent Fractions
Another method involves finding an equivalent fraction with a denominator that is a power of 10. While this isn't always possible (as in this case), understanding the concept is valuable for learning broader fraction manipulation. We can explore this by attempting to find an equivalent fraction with a denominator of 10, 100, 1000, etc. In the case of 3/8, however, no simple multiplication will yield a power of 10 in the denominator. Therefore, this method is less efficient for this specific conversion compared to direct division.
Method 3: Understanding Place Value and Decimal Expansion
This method involves a deeper understanding of place value in the decimal system. Let's break down the fraction 3/8 in terms of its decimal representation.
The fraction 3/8 represents 3 divided into 8 equal parts. We can perform long division to find the decimal equivalent:
0.375
8 | 3.000
2.4
0.60
0.56
0.040
0.040
0.000
This long division shows that 3/8 is exactly equal to 0.375. Adding the whole number 8 gives us the final decimal representation of 8.375.
The Significance of Terminating and Non-Terminating Decimals
It's important to note that the decimal representation of 3/8 is a terminating decimal. This means the decimal expansion ends after a finite number of digits. Not all fractions result in terminating decimals. For example, 1/3 results in a non-terminating, repeating decimal (0.333...). The decimal representation of 3/8, however, is a clean and exact value.
Practical Applications of Decimal Conversions
The ability to convert fractions to decimals is essential in various real-world situations:
- Financial calculations: Calculating interest, discounts, or splitting bills often requires working with decimal representations of fractions.
- Measurement and engineering: Precision measurements and engineering designs frequently involve using decimal numbers. For example, converting fractional dimensions in blueprints to decimal equivalents is a common practice.
- Scientific computations: Many scientific formulas and calculations use decimal numbers, requiring the conversion of fractions to decimal form for accurate results.
- Data analysis: In data analysis and statistics, decimal representation allows for easier manipulation and comparison of numerical data.
- Everyday calculations: Simple tasks like calculating tips, splitting costs, or measuring ingredients in recipes can involve converting fractions to decimals for easier calculations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: Can all fractions be converted to terminating decimals?
- A: No. Fractions with denominators that have prime factors other than 2 and 5 will result in non-terminating, repeating decimals.
-
Q: What if I have a more complex mixed number, like 12 5/16?
- A: The process remains the same. Divide the numerator (5) by the denominator (16) to obtain the decimal equivalent of the fraction. Then add the whole number (12). In this case, 5/16 = 0.3125, and 12 + 0.3125 = 12.3125
-
Q: How can I check my answer?
- A: You can use a calculator to verify your conversion. Alternatively, you can reverse the process: convert the decimal back to a fraction. For 8.375, you can rewrite it as 8 + 375/1000. Simplifying this fraction by dividing both numerator and denominator by 125 yields 3/8, confirming the original mixed number.
-
Q: Why is it important to learn this skill?
- A: The ability to seamlessly convert between fractions and decimals is a fundamental skill that enhances your mathematical proficiency and problem-solving abilities. It opens up opportunities to tackle more complex mathematical problems across diverse fields. It's a cornerstone of numeracy and facilitates clearer understanding in various quantitative situations.
Conclusion: Mastering Decimal Conversions
Converting 8 3/8 to a decimal, resulting in 8.375, is a straightforward process that demonstrates the fundamental relationship between fractions and decimals. Understanding this conversion, along with the concepts of terminating and repeating decimals, empowers you to confidently approach various mathematical problems involving both fractional and decimal representations. Mastering this seemingly simple skill unlocks a greater understanding of numbers and their applications in various fields, significantly enhancing your numerical fluency. The methods outlined above provide a comprehensive approach, allowing you to tackle similar conversions with ease and confidence. Remember to practice regularly to solidify your understanding and improve your speed and accuracy.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 8 3/8 As A Decimal . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.