43 Deg C To F
defexpoindia
Sep 19, 2025 · 5 min read
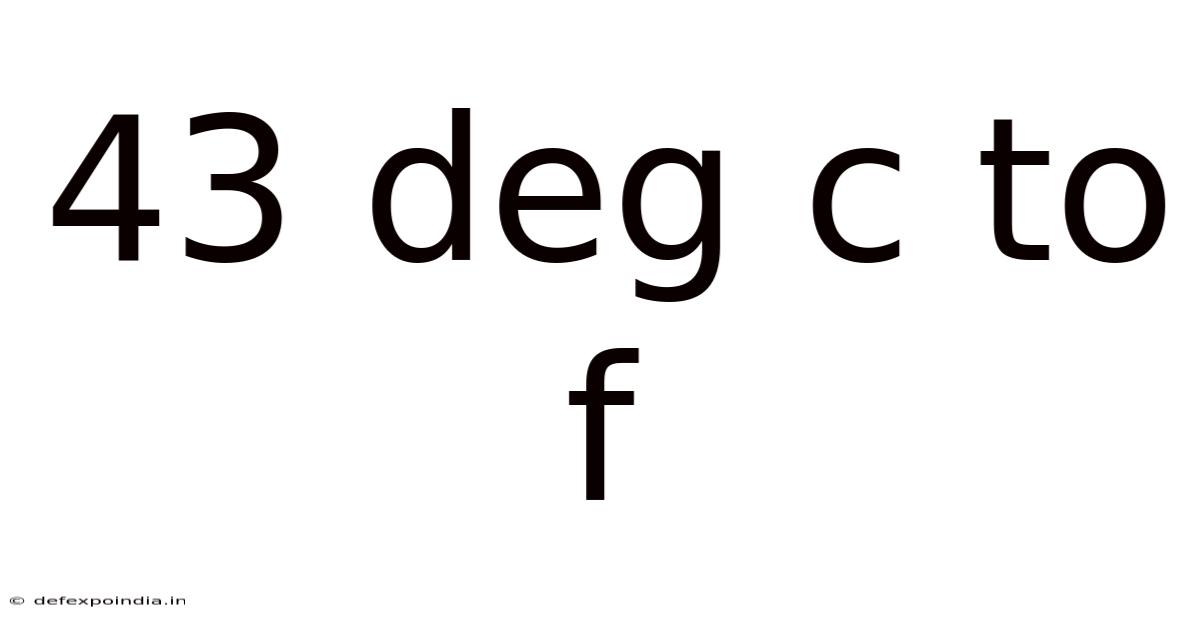
Table of Contents
43°C to °F: Understanding Temperature Conversions and Their Applications
Converting temperatures between Celsius (°C) and Fahrenheit (°F) is a fundamental skill in various fields, from cooking and everyday life to scientific research and engineering. This comprehensive guide will not only show you how to convert 43°C to °F but also delve into the underlying principles, provide multiple methods for conversion, explore the applications of temperature conversions, and answer frequently asked questions. Understanding temperature scales is crucial for accurate communication and effective problem-solving in numerous contexts. This article will equip you with the knowledge and tools to confidently handle temperature conversions.
Understanding Celsius and Fahrenheit Scales
Before diving into the conversion, let's understand the two scales involved:
-
Celsius (°C): Also known as the centigrade scale, Celsius is based on the freezing and boiling points of water at standard atmospheric pressure. Water freezes at 0°C and boils at 100°C. This scale is widely used globally, particularly in scientific contexts.
-
Fahrenheit (°F): Fahrenheit is another temperature scale where water freezes at 32°F and boils at 212°F. It is primarily used in the United States, although its use is decreasing globally.
The difference in the scales stems from the different reference points used to define their zero points and the size of their degree increments.
Converting 43°C to °F: The Calculation
There are two primary methods to convert 43°C to °F: using a formula and using a conversion table (though less precise for specific values).
Method 1: Using the Conversion Formula
The formula for converting Celsius to Fahrenheit is:
°F = (°C × 9/5) + 32
Let's plug in 43°C:
°F = (43 × 9/5) + 32 = (77.4) + 32 = 109.4°F
Therefore, 43°C is equal to 109.4°F.
Method 2: Using a Conversion Table (Approximation)
While less precise for specific values, conversion tables can provide a quick estimate. A comprehensive table would list Celsius values and their corresponding Fahrenheit equivalents. While a complete table is beyond the scope of this article, you can find such tables readily available online or in scientific reference materials. However, using a table for 43°C would only provide an approximate value, making the formulaic approach significantly more reliable for exact conversions.
Applications of Temperature Conversions
The ability to convert between Celsius and Fahrenheit is essential in various fields:
-
Cooking and Baking: Recipes often specify temperatures in either Celsius or Fahrenheit. Accurate conversion is crucial for achieving the desired results. A slight temperature difference can significantly alter the outcome of a dish.
-
Meteorology and Climate Science: Weather reports often provide temperatures in both Celsius and Fahrenheit, catering to diverse audiences. Analyzing climate data requires consistent use of a single scale for accurate comparisons across regions and time.
-
Medicine and Healthcare: Body temperature, medication storage, and various medical procedures require precise temperature control and accurate measurements in either Celsius or Fahrenheit, depending on the context and location.
-
Engineering and Manufacturing: Industrial processes frequently involve precise temperature control. Converting between scales ensures compatibility across different equipment and designs.
-
Scientific Research: Scientific experiments often involve precise temperature measurements, and the ability to convert between scales is essential for data analysis and comparison across studies.
-
Everyday Life: Understanding temperature conversions aids in understanding weather forecasts, setting thermostats, and even planning outdoor activities.
Further Exploration: Understanding the 9/5 Factor
The 9/5 factor in the conversion formula arises from the difference in the size of the degree increments between the Celsius and Fahrenheit scales. One degree Celsius is larger than one degree Fahrenheit. Specifically, a 1°C change corresponds to a 9/5°F change. This accounts for the differing scales' ranges between the freezing and boiling points of water.
Beyond the Conversion: Absolute Temperature Scales
While Celsius and Fahrenheit are widely used, two other scales are crucial in certain scientific contexts:
-
Kelvin (K): Kelvin is an absolute temperature scale where 0 K represents absolute zero, the theoretical lowest possible temperature. It's primarily used in physics and thermodynamics.
-
Rankine (°R): Rankine is another absolute scale used in some engineering applications, particularly in the United States.
Converting between these scales requires different formulas and understanding the concept of absolute zero.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: Why are there two different temperature scales?
A1: Different temperature scales arose historically due to independent development by different scientists. Celsius emerged from the centigrade system, while Fahrenheit's origins lie in a different set of reference points. Both scales have persisted due to their widespread adoption in specific regions.
Q2: Which temperature scale is more accurate?
A2: Both Celsius and Fahrenheit are equally accurate in measuring temperature. Accuracy depends on the quality of the thermometer used, not the scale itself. The choice of scale is largely a matter of convention and regional preference.
Q3: Can I convert from Fahrenheit to Celsius?
A3: Yes, the inverse formula for converting Fahrenheit to Celsius is:
°C = (°F - 32) × 5/9
Q4: What is absolute zero?
A4: Absolute zero (0 K or -273.15°C) is the theoretical lowest possible temperature where all molecular motion ceases. It's a fundamental concept in thermodynamics.
Q5: Are there any online converters for temperature?
A5: Yes, many websites and applications provide online temperature converters that can quickly convert between Celsius, Fahrenheit, Kelvin, and Rankine.
Conclusion
Converting 43°C to 109.4°F is a simple yet crucial skill with wide-ranging applications. Understanding the principles behind the conversion, the different temperature scales, and their uses empowers you to handle diverse situations requiring accurate temperature measurements and conversions. Whether you're a scientist, chef, engineer, or simply someone curious about the world around you, mastering temperature conversions will enhance your understanding of the physical world and improve your problem-solving capabilities. Remember to always use the appropriate formula for precise calculations and choose the most suitable temperature scale for the specific context.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 43 Deg C To F . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.