2000 Watts To Amps 120v
defexpoindia
Sep 23, 2025 · 5 min read
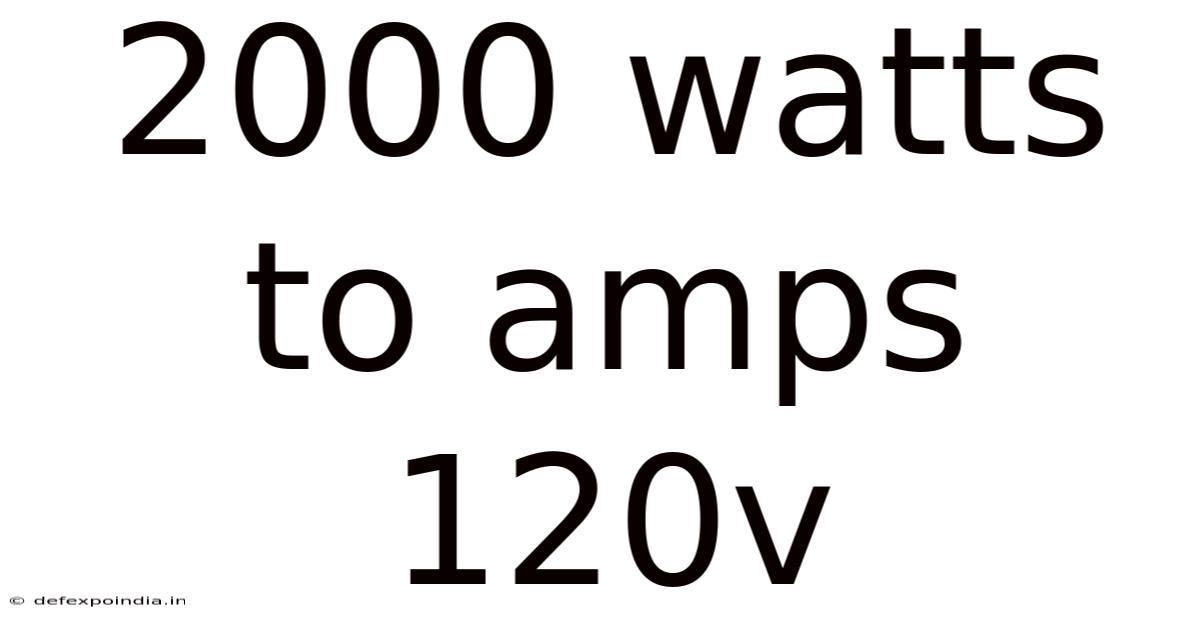
Table of Contents
Understanding the Relationship: 2000 Watts to Amps at 120V
Converting watts to amps is a fundamental concept in understanding electrical power. This article will delve into the calculation of converting 2000 watts to amps at a 120-volt system, explaining the underlying principles and offering practical applications. We'll cover the formula, potential safety concerns, and frequently asked questions, ensuring a comprehensive understanding for anyone dealing with electrical circuits. Understanding this relationship is crucial for choosing the right electrical equipment and ensuring safe operation.
Understanding Watts, Amps, and Volts
Before jumping into the calculation, let's clarify the meaning of these three fundamental electrical units:
-
Watts (W): This unit measures power, representing the rate at which electrical energy is consumed or produced. Think of it as the overall work being done. A higher wattage indicates a higher power consumption.
-
Amps (A): This unit measures current, representing the flow of electrical charge. It's the amount of electricity flowing through a circuit. A higher amperage signifies a stronger flow of electricity.
-
Volts (V): This unit measures voltage, representing the electrical potential difference between two points in a circuit. It's the electrical pressure that pushes the current through the circuit. A higher voltage means a stronger "push."
These three units are interconnected through a simple yet powerful formula.
The Power Formula: Calculating Amps from Watts and Volts
The relationship between watts, amps, and volts is defined by the following formula:
Power (Watts) = Voltage (Volts) × Current (Amps)
Or, more concisely: P = V × I
To find the amperage (I) when you know the power (P) and voltage (V), we rearrange the formula:
Current (Amps) = Power (Watts) / Voltage (Volts)
Or: I = P / V
Calculating 2000 Watts to Amps at 120V
Now, let's apply this formula to convert 2000 watts to amps at 120 volts:
I = 2000 W / 120 V = 16.67 A
Therefore, a 2000-watt appliance operating on a 120-volt circuit will draw approximately 16.67 amps.
Practical Applications and Considerations
This calculation has several practical implications:
-
Circuit Breaker Selection: When installing a new appliance or circuit, you need to ensure the circuit breaker is rated for a sufficient amperage. A 2000-watt appliance at 120V requires a breaker rated for at least 20 amps (it's always recommended to choose a breaker with a higher rating than the calculated amperage to account for surges and variations). Using a lower-rated breaker could lead to tripping or even fire hazards.
-
Wiring Gauge: The correct wire gauge is also critical. The amperage dictates the minimum wire size needed to safely carry the current. Using undersized wire can lead to overheating and potential fire hazards. Consult an electrician or relevant electrical codes to determine the appropriate wire gauge for your specific application.
-
Power Strip Limitations: Many power strips have maximum amperage ratings. You must ensure that the combined amperage of all devices plugged into the power strip doesn't exceed its rating. Overloading a power strip can lead to overheating and fire.
-
Appliance Labels: Always check the appliance's nameplate or label for its wattage and voltage requirements. This information is vital for ensuring safe and proper installation.
-
Power Factor (For AC Circuits): The calculations above assume a power factor of 1.0, which is typical for resistive loads like incandescent light bulbs and heaters. However, many appliances, particularly those with motors (like air conditioners or refrigerators), have a power factor less than 1.0. A lower power factor means the actual current draw will be higher than calculated using the simple formula above. You'll need to incorporate the power factor in your calculations for accurate results.
Safety Precautions When Working with Electricity
Working with electricity can be dangerous if not handled properly. Always follow these safety precautions:
-
Turn off the power: Before working on any electrical circuit, always turn off the power at the breaker box.
-
Use appropriate tools: Use insulated tools to prevent electrical shocks.
-
Don't overload circuits: Never overload electrical circuits beyond their rated capacity.
-
Consult a professional: If you're not comfortable working with electricity, consult a qualified electrician. Incorrect wiring or circuit installation can lead to serious injury or property damage.
-
Understand your local electrical codes: Your area will have building codes regarding electrical installation. Following these codes is essential for safety and compliance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What happens if I use a circuit breaker with a lower amperage rating than required?
A1: Using a lower-rated circuit breaker will likely lead to the breaker tripping frequently, interrupting the power supply to the appliance. In severe cases, it could lead to overheating of the wiring and potentially a fire.
Q2: Can I use a 15-amp circuit for a 2000-watt appliance at 120V?
A2: No, a 15-amp circuit is insufficient for a 2000-watt appliance at 120V (requiring approximately 16.67 amps). Using a 15-amp circuit would overload the circuit and pose a significant fire risk.
Q3: What is the difference between a 120V and a 240V circuit?
A3: The voltage difference significantly impacts the amperage draw. A 2000-watt appliance on a 240V circuit would draw only approximately 8.33 amps (2000W / 240V). Higher voltage requires lower amperage for the same power output. This is why higher-voltage circuits are used for larger appliances.
Q4: What if my appliance has a motor? Will the actual amperage draw be higher?
A4: Yes, appliances with motors often have a power factor less than 1.0. This means the actual current draw will be higher than the calculated value. Consult the appliance's specifications for the correct amperage rating.
Q5: How can I accurately determine the amperage draw of an appliance?
A5: The most accurate way is to use a clamp meter, a specialized tool that measures current without interrupting the circuit. Alternatively, the appliance's nameplate should provide this information.
Conclusion
Converting 2000 watts to amps at 120V is a straightforward calculation using the formula I = P/V, resulting in approximately 16.67 amps. However, understanding the implications of this calculation is crucial for ensuring electrical safety. Always choose appropriately rated circuit breakers, wiring, and power strips. Remember that safety should be your top priority when working with electricity, and consulting a qualified electrician is recommended if you have any doubts or uncertainties. By carefully considering these factors, you can safely and effectively manage your electrical systems.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 5 5kg In Pounds
Sep 23, 2025
-
179cm In Ft And Inches
Sep 23, 2025
-
0 4 Repeated As A Fraction
Sep 23, 2025
-
7 8 As A Percentage
Sep 23, 2025
-
Cm To Lbs Conversion Calculator
Sep 23, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 2000 Watts To Amps 120v . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.