13c Is What In Fahrenheit
defexpoindia
Sep 14, 2025 · 5 min read
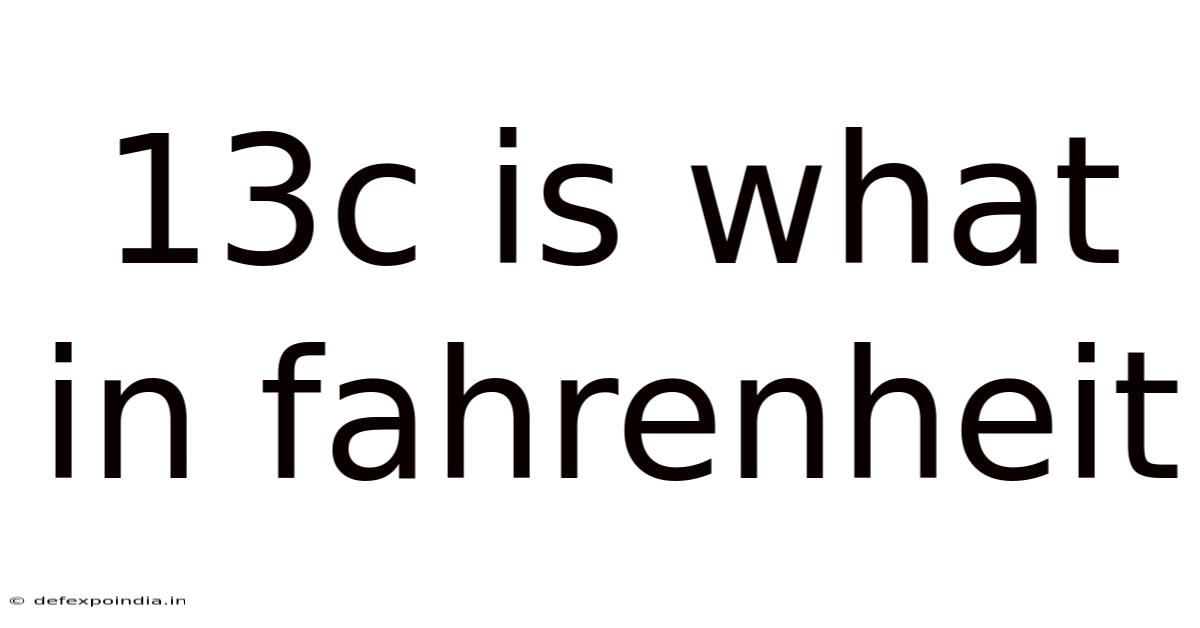
Table of Contents
13°C is What in Fahrenheit? Understanding Temperature Conversions
Understanding temperature conversions between Celsius (°C) and Fahrenheit (°F) is a fundamental skill with applications ranging from everyday life to scientific research. This comprehensive guide will not only answer the question "13°C is what in Fahrenheit?" but also delve into the underlying principles, provide a step-by-step calculation, explore real-world applications, and address frequently asked questions. We'll also examine the history and significance of both scales.
Introduction: Celsius vs. Fahrenheit
The world uses two primary temperature scales: Celsius (°C) and Fahrenheit (°F). Celsius, also known as the centigrade scale, is based on the freezing and boiling points of water at 0°C and 100°C, respectively, at standard atmospheric pressure. Fahrenheit (°F), on the other hand, sets the freezing point of water at 32°F and the boiling point at 212°F. This difference stems from historical development and differing scientific approaches. Understanding the conversion between these scales is crucial for accurate communication and data interpretation across various fields.
1. Calculating 13°C in Fahrenheit: The Formula
The conversion from Celsius to Fahrenheit involves a simple yet crucial formula:
°F = (°C × 9/5) + 32
Let's apply this formula to convert 13°C to Fahrenheit:
°F = (13°C × 9/5) + 32
°F = (23.4) + 32
°F = 55.4
Therefore, 13°C is equal to 55.4°F.
2. Step-by-Step Conversion Process
To make the conversion process clearer, let's break it down into individual steps:
-
Multiply the Celsius temperature by 9/5: This step adjusts for the different scale increments between Celsius and Fahrenheit. Multiplying by 9/5 (or 1.8) accounts for the fact that a 1°C change is equivalent to a 1.8°F change.
-
Add 32: This step accounts for the difference in the zero points of the two scales. The Fahrenheit scale starts at 32°F, which corresponds to 0°C. Adding 32 shifts the Fahrenheit reading to the correct base point.
3. Real-World Applications of Temperature Conversions
The ability to convert between Celsius and Fahrenheit is essential in numerous contexts:
-
International Collaboration: Scientific research, international trade, and global communication frequently involve exchanging temperature data. Consistent conversion ensures accuracy and avoids misunderstandings.
-
Cooking and Baking: Many recipes specify temperatures in either Celsius or Fahrenheit. Accurate conversion prevents baking mishaps and ensures consistent results.
-
Weather Reporting: Weather forecasts are often provided in both scales to cater to diverse audiences and regions with differing preferences.
-
Medical Applications: Body temperature measurements are crucial in healthcare. The ability to convert between scales ensures accurate diagnosis and monitoring.
-
Industrial Processes: Many industrial processes, particularly in manufacturing and chemical engineering, rely on precise temperature control, demanding accurate conversions between Celsius and Fahrenheit.
-
Climate Science: Studying climate change and interpreting climate data necessitate seamless temperature conversion between Celsius and Fahrenheit to ensure consistent analysis across datasets and geographical regions.
4. The History of Celsius and Fahrenheit Scales
Understanding the conversion is also enriched by understanding the history behind the two scales.
-
Celsius (Centigrade): The Celsius scale is attributed to Anders Celsius, a Swedish astronomer. His original scale was inverted (0°C was the boiling point and 100°C was the freezing point), but it was later reversed to its current form.
-
Fahrenheit: Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit, a German physicist, developed the Fahrenheit scale. He based his scale on a mixture of ice, water, and ammonium chloride, establishing 0°F as the freezing point of this mixture. The scale was later refined, with the freezing and boiling points of water established as 32°F and 212°F, respectively.
The differences in their origins account for the unique characteristics of each scale and the need for a conversion formula.
5. Beyond the Basics: Advanced Temperature Concepts
While the Celsius to Fahrenheit conversion is fundamental, several more advanced concepts broaden our understanding of temperature:
-
Kelvin (K): The Kelvin scale is the absolute temperature scale, where 0 K represents absolute zero, the theoretical point where all molecular motion ceases. This scale is extensively used in scientific applications. Converting between Celsius and Kelvin is simpler: K = °C + 273.15.
-
Rankine (R): The Rankine scale is the absolute temperature scale based on Fahrenheit. Its zero point coincides with absolute zero. Conversion from Fahrenheit is straightforward: R = °F + 459.67.
-
Temperature Gradient: In many applications, understanding the rate of temperature change (gradient) is crucial. This involves calculating the change in temperature over a given distance or time.
-
Heat Transfer: Temperature is intrinsically linked to heat transfer mechanisms like conduction, convection, and radiation. Understanding these processes is critical in fields like engineering and meteorology.
6. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
Why are there two different temperature scales? The existence of both Celsius and Fahrenheit scales reflects historical developments and differing scientific conventions. While Celsius is more widely used internationally, Fahrenheit remains prevalent in some regions.
-
Which scale is more accurate? Both scales are equally accurate in measuring temperature; the difference lies in their scales and zero points. However, the Kelvin scale provides a more fundamental measure of temperature.
-
Are there any other temperature scales? Yes, several other scales exist, including the Rømer scale, the Delisle scale, and the Réaumur scale, though they are less commonly used.
-
Can I convert Fahrenheit to Celsius? Yes, the reverse conversion is: °C = (°F - 32) × 5/9.
-
How do I convert between Celsius and Kelvin? °C = K - 273.15, and K = °C + 273.15
7. Conclusion: Mastering Temperature Conversions
Mastering temperature conversions between Celsius and Fahrenheit is a valuable skill with far-reaching applications. This guide provided a detailed explanation of the conversion process, its real-world relevance, and an insight into the historical context of the temperature scales. Understanding these concepts not only answers practical questions like "13°C is what in Fahrenheit?" but also enhances your understanding of fundamental scientific principles related to temperature measurement and its significance in diverse fields. The information presented here serves as a foundation for further exploration of thermodynamics and other related scientific disciplines. By grasping the fundamentals, you are well-equipped to confidently navigate various situations requiring temperature conversions and appreciate the scientific context behind these everyday calculations.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 13c Is What In Fahrenheit . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.