101 4 F To C
defexpoindia
Sep 21, 2025 · 6 min read
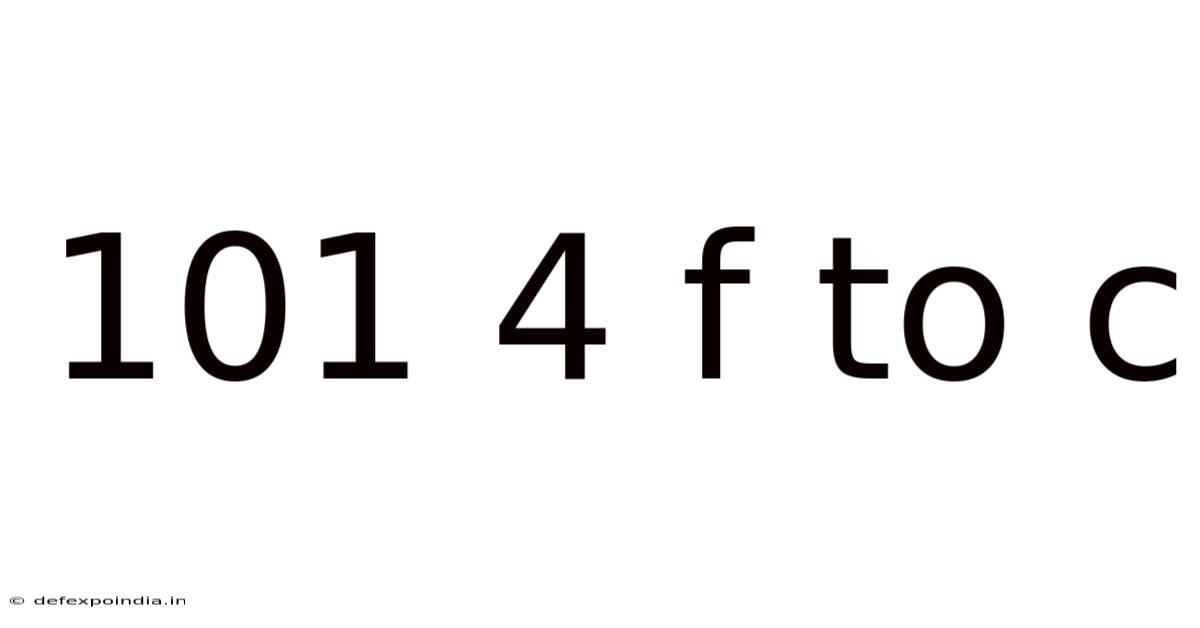
Table of Contents
101 on Converting Fahrenheit to Celsius: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding how to convert Fahrenheit to Celsius is a fundamental skill in many fields, from cooking and baking to science and meteorology. This comprehensive guide will take you beyond a simple formula, exploring the history behind these temperature scales, the nuances of conversion, and practical applications to solidify your understanding. Whether you're a student struggling with unit conversions or a curious individual wanting to deepen your knowledge, this guide offers a complete and accessible approach to mastering Fahrenheit to Celsius conversions.
Introduction: The Two Giants of Temperature Measurement
The world uses two primary temperature scales: Fahrenheit (°F) and Celsius (°C), also known as Centigrade. While Celsius is the internationally preferred system used in most scientific contexts and daily life globally, Fahrenheit remains prevalent in the United States and a few other countries. Understanding how to convert between these two scales is crucial for seamless communication and accurate interpretation of temperature readings. This guide will equip you with the tools and knowledge necessary to effortlessly convert between Fahrenheit and Celsius, regardless of the context.
Understanding the Scales: A Historical Perspective
Before diving into the conversion methods, let's briefly explore the historical context of these scales. The Fahrenheit scale, developed by Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit in the early 18th century, initially used a zero point based on a mixture of ice, water, and ammonium chloride. Later refinements set the freezing point of water at 32°F and the boiling point at 212°F, at standard atmospheric pressure.
The Celsius scale, devised by Anders Celsius in the mid-18th century, initially defined the boiling point of water as 0°C and the freezing point as 100°C (this was later reversed). The Celsius scale, also known as the centigrade scale due to its 100-degree interval between the freezing and boiling points of water, is now based on the triple point of water (0.01°C) and absolute zero (-273.15°C). Understanding this historical context helps appreciate the logic behind the conversion formulas.
The Fundamental Formula: From Fahrenheit to Celsius
The most straightforward way to convert Fahrenheit (°F) to Celsius (°C) is using a simple formula:
°C = (°F - 32) × 5/9
This formula elegantly captures the relationship between the two scales. Let's break it down step-by-step:
-
Subtract 32: This step accounts for the difference in the freezing point of water (32°F vs 0°C). Subtracting 32 from the Fahrenheit temperature aligns the scales at the freezing point.
-
Multiply by 5/9: This step adjusts for the different scales' size. The Celsius scale has a smaller degree interval than Fahrenheit. Multiplying by 5/9 (or 0.5556) reduces the numerical value to reflect this difference.
Example: Let's convert 68°F to Celsius.
-
68°F - 32°F = 36°F
-
36°F × 5/9 = 20°C
Therefore, 68°F is equivalent to 20°C.
Beyond the Formula: Understanding the Conversion Process
While the formula is efficient, understanding the underlying logic enhances comprehension. The formula's steps effectively re-scale and re-zero the Fahrenheit temperature to fit the Celsius framework. The subtraction of 32 shifts the zero point, and the multiplication by 5/9 adjusts the scale's granularity.
Practical Applications: Real-World Examples
Let's explore some practical scenarios where converting Fahrenheit to Celsius is essential:
-
Cooking and Baking: Recipes often specify temperatures in either Fahrenheit or Celsius. Accurately converting temperatures ensures consistent results. For example, a recipe calling for 350°F (177°C) requires accurate conversion for successful baking.
-
Weather Forecasting: International weather reports frequently use Celsius. Converting Fahrenheit forecasts to Celsius helps understand global weather patterns and comparisons.
-
Science and Engineering: Scientific experiments and engineering applications often require precise temperature control and reporting, necessitating accurate conversions between Fahrenheit and Celsius.
-
Medical Applications: Body temperature is frequently measured in both scales. Understanding the conversion is crucial for accurate medical diagnosis and treatment.
Mastering the Conversion: More Examples and Practice
Let’s practice with a few more examples:
-
Convert 212°F to Celsius: (212 - 32) × 5/9 = 100°C (Boiling point of water)
-
Convert 32°F to Celsius: (32 - 32) × 5/9 = 0°C (Freezing point of water)
-
Convert 98.6°F to Celsius: (98.6 - 32) × 5/9 = 37°C (Normal human body temperature)
-
Convert -4°F to Celsius: (-4 - 32) × 5/9 = -20°C
The more you practice, the more intuitive the conversion becomes. Try converting various Fahrenheit temperatures to Celsius to build confidence and fluency.
The Reverse Conversion: From Celsius to Fahrenheit
Knowing how to convert from Celsius to Fahrenheit is equally important. The reverse formula is:
°F = (°C × 9/5) + 32
This formula reverses the steps in the Fahrenheit to Celsius conversion. The multiplication by 9/5 scales the Celsius temperature up to Fahrenheit's larger degree interval, and adding 32 shifts the zero point to align with the Fahrenheit scale.
Example: Convert 20°C to Fahrenheit:
-
20°C × 9/5 = 36°F
-
36°F + 32°F = 68°F
Therefore, 20°C is equivalent to 68°F.
Dealing with Negative Temperatures
The conversion formulas work equally well with negative temperatures. Remember to follow the order of operations (parentheses first, then multiplication, then addition or subtraction). For instance, converting -40°C to Fahrenheit yields:
(-40 × 9/5) + 32 = -40°F. This is a unique point where both scales coincide.
Advanced Considerations: Significant Figures and Precision
In scientific and engineering applications, paying attention to significant figures and precision is crucial. The number of significant figures in your answer should reflect the precision of the input temperature. For example, if you are given a temperature of 75.2°F, your answer should ideally maintain a similar level of precision in Celsius.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
Q: Why are there two different temperature scales? A: Different scales arose historically due to varying scientific approaches and regional preferences.
-
Q: Which scale is more accurate? A: Both scales are equally accurate for measuring temperature. The choice depends on the context and regional conventions.
-
Q: Can I use a conversion calculator? A: Yes, many online calculators and apps readily perform Fahrenheit to Celsius conversions. However, understanding the underlying formula remains beneficial.
-
Q: What is the absolute zero point in Celsius and Fahrenheit? A: Absolute zero is -273.15°C and -459.67°F. This represents the theoretical lowest possible temperature.
-
Q: What is the difference between Celsius and Centigrade? A: Celsius and Centigrade are essentially the same scale. The term "centigrade" is older and less commonly used now.
Conclusion: Mastering Temperature Conversions
Mastering Fahrenheit to Celsius conversions is a valuable skill applicable across various domains. While the formulas are straightforward, a deeper understanding of the underlying principles and historical context enhances comprehension and application. Practice makes perfect—the more you work with the formulas and apply them to real-world examples, the more confident and fluent you will become in navigating the world of temperature measurements. This guide has provided you with the tools and knowledge to confidently tackle any Fahrenheit to Celsius conversion. Now, go forth and conquer the world of temperatures!
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 101 4 F To C . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.